Related Technical Articles
Disadvantageous of Mal-odors during Recycling
- Worker Health and Safety
Exposure to unpleasant and potentially harmful odors can cause headaches, nausea and respiratory distress among workmen. This may result in decreased productivity and concern among workmen. - Product Quality and Consumer Acceptance
The final products made from recycled polymers may have persistent unpleasant odors. This may not be acceptable to consumers resulting in reduced demand for recycled items and hampering the company’s credibility and reliability. - Environmental Impact
Some VOCs may release unwanted intermediates which may cause air pollution and harm the environment. - Process Efficiency
Dealing with odors can complicate the recycling process. It may need additional steps such as washing, deodorizing and using odor removal additives. It increases the cost and complexity of recycling operations. - Regulatory Compliance
Stringent regulations regarding emissions and workplace safety may require recycling facilities to invest in additional set up for odor control. This legal compliance requirement may increase the operational costs.
Odor Removing Techniques
There are various advanced purification and odor removal techniques developed over the years for removing mal-odors during polymer processing. The primary mechanical pre-treatment method includes shredding of plastic into smaller pieces, washing the shredded material with water & drying the shredded material before moulding. This pre-treatment is followed by 4 main techniques, namely Adsorption, Thermal Treatment, Chemical Treatment and Deoderization. These techniques help to improve the quality of the recycled polymers and reduce unpleasant odors on the processing lines.
- Adsorption
This involves using adsorbents that trap the VOCs and odorous compounds and do not
release them back into the atmosphere. In simple words, Adsorption is the adhesion of
atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. The surface is
called an ‘adsorbent’ and the substance getting adhered to the surface is called an
‘adsorbate’. - Thermal Treatment
This involves using heat processes to volatilise and eliminate the odorous compounds. - Chemical Treatment
This involves using chemical scrubbing compounds which react with the mal-odors and
oxidise them. It describes the degree of loss of electrons of an atom in a chemical
compound. Oxidation chemically removes the mal-odor compounds from the molten
polymer mix. - Deodorizing Agents
These are chemical compounds that are added as additives to neutralise or mask the mal
odors. There is a growing trend of using bio-based additives that contain enzymes and
natural extracts that break down or mask the odorants.
Odor Removing Compounds
Chemical actives used in Odor Removing Additives are selected based on specific types of odors they are expected to target and the nature of the polymers being treated. The actives include adsorbents, deodorizers, cyclodextrins, metal oxides, antioxidants, acid neutralizers, essential oils, enzymes etc.
- Adsorbents
Activated Carbon is one of the most widely used adsorbant due to its high surface area and porosity. It adsorbs VOCs and other odorants very effectively. Zeolites are aluminosilicate minerals which effectively trap and hold the VOCs due to their microporous nature. Silica Gel is also an effective adsorbent commonly used during recycling processes to remove foul odors. - Deoderizers
Potassium Permanganate reacts with odor causing substances to neutralise them from the processing atmosphere. - Cyclodextrins
Cyclic Oligosaccharides form complexes with odor molecules, encapsulate and neutralize them. - Metal Oxides
Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide catalyse the break-down of VOCs and other odorants thereby reducing the mal-odor. - Antioxidants
Compounds like Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) prevent the oxidation of polymer components. This reduces the formation of degradation byproducts during polymer processing. - Acid Neutralizers
Compounds like sodium bicarbonate neutralize the acidic odoriferous molecules to control their odor. - Essential oils
Aromatic oils like rosemary oil, wintergreen oil, vanillin, lemongrass oil etc are natural extracts which can neutralise or mask the odors due to their own antimicrobial or perfumery property respectively. - Enzymes
Biological molecules like enzymes break down the mal-odor molecules to non-odor
NICHEM’s Odor Control Technologies
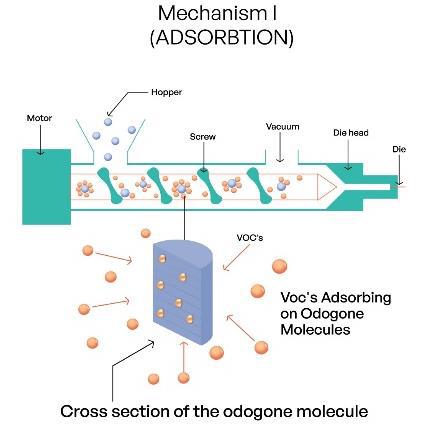
Fig 1: Adsorption Mechanism of OdoGone
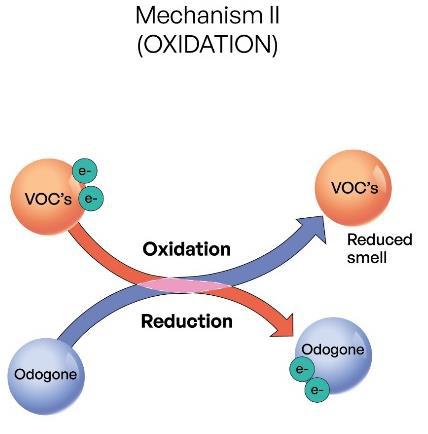
Fig 2: Oxidation Mechanism of OdoGone
- Odor Removal by Adsorption
During recycling, as the shredded polymer granules pass through the extruder, they melt due to the heat. This generates volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Some of these
compounds are adsorbed on the surface of OdoGone molecules as depicted in Fig 1. Thus, the foul odors during processing are reduced significantly. The active compounds in OdoGone are selected based on their thermal stability at high temperatures as in the barrel of the extruder. The period of adsorption of mal-odors from the finished material cannot be defined due to the varied chemical nature of the VOCs. However, the finished material/article prepared from recycled plastic may develop some odor due to trigger by external factors like heat. Data needs to be generated using accelerated UV/Heat stability testing to analyse the reoccurrence of mal-odor in different types of shredded waste from the processors. - Odor Removal by Oxidation
During recycling, while some VOCs get adsorbed, some of them get oxidised by losing electrons to the active molecules of OdoGone present in the hot molten mixture. The oxidation of VOCs reduces the mal-odor of the molten mixture. In this process, OdoGone gets reduced by gaining the electrons from the VOCs as depicted in Fig 2. Unlike physical adhesion of VOCs in Adsorption mechanism, Oxidation process chemically removes the mal-odors from the polymer mix.
About NICHEM
Long-standing Specialty Chemicals player with ISO 9001:2015 certification and a history of providing specialty solutions for over 25 years. The company is headed by senior chemical industry specialists with the combined expertise of more than 100 years. With an emphasis on eco-friendly, non-toxic products, the company’s primary strength is research, development, and customization. More information on NICHEM can be found at https://nichem.solutions.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adsorption#cite_note-11
- Guruge, Amila Ruwan (2021-02-17). “Absorption Vs Adsorption”. Chemical and Process Engineering. Retrieved 2023-11-26.)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidation_state
- https://www.polymerupdateacademy.com/WeeklyInsights/Details/1271749#:~:text=Volati le%20substances