Related Blogs
Safe drinking water is one of the most essential requirements to live a healthy life. Consumption of unsafe water leads to gastroenteric diseases, and health hazards related to chemical contaminants. The advent of water purification technology has provided efficient ways to avail safe and clean drinking water. Reverse Osmosis (RO) is one of the most popular technologies used for water purification around the world for water sources with higher concentrations of salts.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
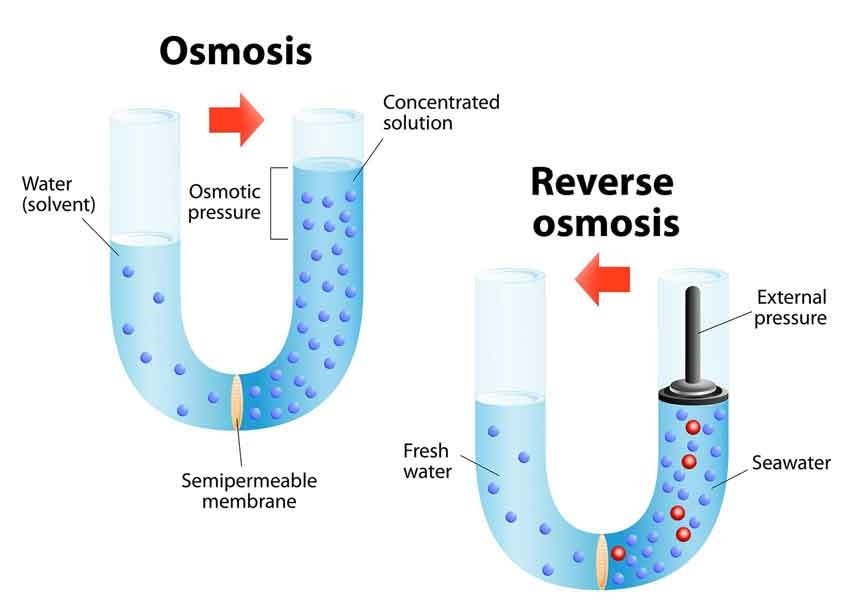
Migration of water from solution with low salt content to solution with higher salt content, as occurs in plants through the root system, is termed osmosis.
In reverse osmosis, water is forced in the opposite direction to its natural osmotic flow. Here, water is pushed through a semi-permeable membrane at high pressure. The RO membrane is a thin film composite and semi-permeable layer with pores in it. The size of these pores is about a million times smaller than the width of a human hair.
In comparison to this, the bacteria and viruses are too large in size, about 5000 times, to pass through these pores. As a result of this, the smaller water molecules pass through while bacteria and viruses get filtered out due to their larger size. This process also filters out traces of heavy metals, inorganic constituents and pesticides to give clean, uncontaminated water.
History of Reverse Osmosis
The process of osmosis was first observed in a laboratory in 1748 by a French clergyman and physicist Jean-Antoine Nollet. He showed how a solvent can pass through a semipermeable membrane because of the natural osmotic pressure. For the next 200 years, the process of osmosis was only observed in the laboratory.
It wasn’t until 1949 that it was used by the University of California at Los Angeles to remove salt from seawater. During the 1960s, an Indian scientist Dr. Srinivasa Sourirajan developed a desalination membrane that allowed water to pass through while selectively separating sodium chloride and dissolved solids using cellulose acetate. Sourirajan’s discovery became the backbone of RO systems developed since then and gave him the title of “Father of Reverse Osmosis”.
By the late 1970s, the process of reverse osmosis was being used on a large scale to purify water in the USA.
As the technology became more advanced and accessible for public use, RO machines spread to various parts of the world. Presently, RO systems are used for various industrial, residential, commercial, medical and scientific purposes.
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis offers various advantages over other techniques used for water purification like chemical, carbon filtration and physical filtration etc. Some of the major benefits of RO are listed below:
- Filters out most contaminants: Reverse osmosis removes most contaminants from water including bacteria, asbestos and lead. Apart from this, the filter membrane used for RO can also remove dissolved substances and minerals from water.
- Quality of water: The quality of RO purified water is suitable for many domestic purposes. As it is free of minerals, its taste is suitable for cooking. The purity of RO water also makes it suitable for inhabiting aquatic pets like fish.
Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis
Besides the many advantages of RO as a water purification system, it also comes with some disadvantages. They are listed below:
- Expensive installation: The initial cost of installation of RO systems makes it inaccessible to a lot of people who are unable to afford it. Apart from installation, RO systems also require regular maintenance while in use which requires professional help.
- Reduces pH and removes essential minerals: RO purification removes many healthy minerals like calcium, magnesium and potassium along with harmful contaminants. Besides this, the removal of minerals also reduces the pH of water making it more acidic.
- Wastage of water: RO purification wastes about three times the amount of water it purifies. So, for every 1 liter of purified water, an average RO system wastes about three liters of water. This leads to higher water bills and can lead to shortage in times of water scarcity. In order to reduce this wastage, the World Economic Forum has launched a project to reuse 20 lakh liters of water wasted by RO systems for domestic purposes including cleaning utensils, clothes, cars, watering plants etc.
How to overcome these disadvantages?
Some of the disadvantages listed above can be overcome with the help of the latest technology. The problem of mineral loss can be overcome by using doser cartridges. This includes alkaline cartridges, mineralized cartridges and booster cartridges.
The RO purification also removes some useful minerals along with the harmful contaminants. The use of alkaliser cartridges can retain essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. This can help to soothe the acidic nature of water and increase its pH value. This addition of minerals can provide various health benefits to the body including improved bone health, better metabolism and control blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol.
Despite some of its disadvantages, RO purification is a very useful and accessible way to avail clean and healthy drinking water. The advances in the underlying technology and better use of wasted water are helping to overcome its disadvantages rapidly and make it more practical and environment-friendly.
About NICHEM
Long-standing Specialty Chemicals player with ISO 9001:2015 certification and a history of providing specialty solutions for over 25 years. The company is headed by senior chemical industry specialists with the combined expertise of more than 100 years. With an emphasis on eco-friendly, non-toxic products, the company’s primary strength is research, development, and customization. More information on NICHEM can be found at https://nichem.solutions.