Related Blogs
Water is a vital resource for sustaining life, and in India, a country with a population of over 1.3 billion people, ensuring access to safe and clean water is of utmost importance. However, with the ever growing strength of population, the current state of water resources in India poses significant challenges in terms of accessibility and safety.
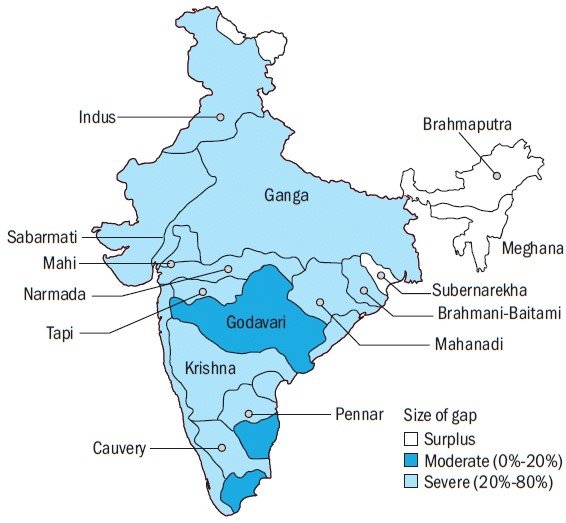
Image source: Research Gate
The figure above depicts the potential gap between the supply and demand of water in the year 2030 in India. The gap between the need for clear and safe water is increasing at an alarming rate, which is a definite call for immediate action. Due to increase in pollution and ground water depletion, most of the states in India are facing a severe gap between supply and demand of water.
Where does India get its water supply?
Being a vast country, India accounts for about 2% of the world’s surface area and 4% of the world’s sources of water. Some of the major sources of water in India are available through surface water. This includes rivers, lakes, ponds and tanks. Groundwater, too, accounts for a valuable source of water, especially in Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
The amount of use of groundwater is generally higher in river basins in the north-western region and a few parts in the south of India.
However, not only is the water supply getting more and more scarce, what is cause for concern is the increase in contamination, too.
What is contamination?
Water contamination refers to the presence of harmful substances in water that can negatively affect human health and the ecosystem. Contaminants can include physical, chemical, and biological substances that find their way into water sources through various means such as industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and inadequate sanitation systems. Common types of water contaminants include heavy metals, harmful chemicals, pesticides, pathogens, organic pollutants, and nutrients.
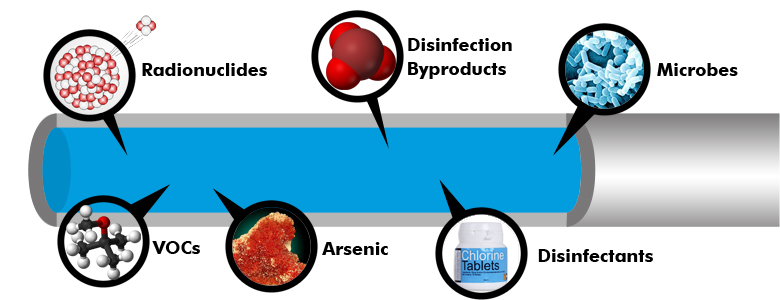
Image source: freedrinkingwater.com
Why is contamination of water a threat?
Water contamination has far-reaching consequences for both human and environmental well-being in India. Firstly, it poses a severe threat to human health, leading to diseases such as diarrhea, cholera, typhoid, and various other waterborne illnesses. Prolonged exposure to contaminated water can also result in chronic health conditions, including kidney and liver damage, neurological disorders, and certain types of cancer.
The impact of water contamination extends beyond human populations. Wildlife, particularly aquatic organisms, suffer from the presence of pollutants in water bodies. Contaminated water disrupts ecosystems, affecting the biodiversity and delicate balance of natural habitats. Furthermore, contaminated water adversely affects the environment and climate by contaminating soil, reducing crop yields, and contributing to water scarcity.
What does the present look like for India?
Various regions in India face the brunt of water contamination. According to studies conducted by the Central Ground Water Board, several states, including Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Rajasthan, and West Bengal, have reported high levels of contamination in their groundwater sources.
Industrial and agricultural activities, coupled with inadequate waste management systems, have contributed to the deteriorating quality of water resources in these regions.
Which are the most harmful contaminants?
There are many harmful contaminants present in water that pose a challenge to human health. Although contaminants like organic matter, microorganisms, and hardness can be eliminated with the help of present filtration systems. The real problem lies with the elimination of heavy metals from the water like Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Fluoride, Arsenic, Nitrate, etc. The most prone heavy metal contamination which India suffers are listed below:
- Flouride: Fluoride is naturally present in igneous and sedimentary rocks through which it becomes a part of ground water. High concentration of fluoride in water can cause many health hazards like dental and skeletal fluorosis, arthritis and bone damage. 13 Indian states have an above normal concentration of fluoride in their groundwater. Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan and Karnataka have the highest concentration. The rural areas face an even bigger challenge as the contamination in these regions is 1.85 times higher than urban areas.
- Arsenic: Arsenic is present naturally in ground water and gets added to water due to industrial processes like processing of glass, pigments, textiles, paper, metal adhesives, wood preservatives and ammunition. Long-term consumption of arsenic can lead to dangerous skin conditions like skin cancer and cause damage to bladder and lungs. Prominent Indian states like West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Manipur and Chhattisgarh have the maximum number of districts with above normal concentrations of arsenic in their ground water.
- Nitrate: Nitrate gets added to ground water from nitrate sources like nitrogen rich wastes and fertilizers. Long term consumption of nitrate in drinking water has found to cause major health hazards like colorectal cancer, thyroid disease and neural tube defects. An above normal concentration of nitrate has been found in the ground water of Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Delhi, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
Taking action for the future

Image source: Give.do
Recognizing the severity of the water contamination issue, India has implemented several initiatives to address this pressing challenge. The Government of India has launched the National Water Quality Sub-Mission under the National Rural Drinking Water Program to provide safe drinking water to rural communities. This program aims to assess and monitor water quality, strengthen water testing laboratories, and promote behavior change towards safe water practices.
Additionally, India is focusing on promoting sustainable water management practices. Efforts are being made to improve wastewater treatment and reuse systems, encourage rainwater harvesting, and implement stringent regulations on industrial and agricultural practices to minimize water pollution. Activation is also taking place by non-government organizations, all striving to help India have more clean water.
You can make a change too!
- Regularly test the quality of their drinking water to identify potential contaminants.
- Use household water filtration systems.
- Practice responsible use of water, avoiding excessive wastage and pollution.
- Use adsorbers to extract iron and arsenics from your water.
- Promote awareness and education about water pollution and its consequences in local communities.
About NICHEM
Long-standing Specialty Chemicals player with ISO 9001:2015 certification and a history of providing specialty solutions for over 25 years. The company is headed by senior chemical industry specialists with the combined expertise of more than 100 years. With an emphasis on eco-friendly, non-toxic products, the company’s primary strength is research, development, and customization. More information on NICHEM can be found at https://nichem.solutions.